Journal Description
Current Oncology
Current Oncology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal published online by MDPI (from Volume 28 Issue 1-2021). Established in 1994, the journal represents a multidisciplinary medium for clinical oncologists to report and review progress in the management of this disease. The Canadian Association of Medical Oncologists (CAMO), the Canadian Association of Psychosocial Oncology (CAPO), the Canadian Association of General Practitioners in Oncology (CAGPO), the Cell Therapy Transplant Canada (CTTC), the Canadian Leukemia Study Group (CLSG) and others are affiliated with the journal and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Oncology)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
2.8 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.9 (2023)
Latest Articles
Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with Late Radiation-Associated Dysphagia: Swallowing Safety, Efficacy, and Dysphagia Phenotype
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 233; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040233 (registering DOI) - 16 Apr 2025
Abstract
Late radiation-associated dysphagia (late-RAD) remains a challenge in head and neck cancer (HNC) survivorship, despite advancements in treatment methods. Although Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) stands as the preferred diagnostic approach for oropharyngeal dysphagia assessment in the HNC population, current studies lack
[...] Read more.
Late radiation-associated dysphagia (late-RAD) remains a challenge in head and neck cancer (HNC) survivorship, despite advancements in treatment methods. Although Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing (FEES) stands as the preferred diagnostic approach for oropharyngeal dysphagia assessment in the HNC population, current studies lack a FEES-derived swallowing parameter characterization and phenotypic classification within this specific cohort. This study sought to employ FEES-based assessment to characterize swallowing safety and efficacy profiles, identify distinct phenotypes in HNC patients suffering from late-RAD, and examine potential correlations between safety and efficacy parameters. A retrospective analysis included twenty-four post-radiotherapy HNC patients evaluated using standardized FEES protocols across three bolus consistencies (liquid, semisolid, and solid). Swallowing safety was quantified using the Penetration–Aspiration Scale (PAS), while efficacy was measured via the Yale Pharyngeal Residue Severity Rating Scale (YPRSRS). Additionally, six distinct dysphagia phenotypes were characterized within the cohort. Propulsion deficit was the predominant phenotype (92%), followed by delayed pharyngeal phase (37.5%) and protective deficit (25%), with 46% of patients exhibiting multiple phenotypes. Unsafe swallowing occurred most frequently with liquid consistency (62.5%), while residue was most prevalent with semisolid (82.6% valleculae, 52.2% pyriform sinuses) and solid consistencies (92.3% valleculae, 53.8% pyriform sinuses). Significant correlations were found between penetration–aspiration and pharyngeal residue scores across consistencies (p < 0.05). FEES examination revealed distinct phenotypes in late radiation-associated dysphagia, with a predominance of propulsion deficit and significant interdependence between safety and efficacy parameters.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Head and Neck Oncology)
Open AccessReview
Advances in Targeted and Systemic Therapy for Salivary Gland Carcinomas: Current Options and Future Directions
by
Sushanth Sreenivasan, Rahim A. Jiwani, Richard White, Veli Bakalov, Ryan Moll, Joseph Liput and Larisa Greenberg
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 232; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040232 - 16 Apr 2025
Abstract
Salivary gland carcinomas (SGCs) represent a rare and heterogeneous group of malignancies accounting for 3–6% of all head and neck cancers. While surgical resection and radiotherapy remain the standard for locoregional control, systemic treatment is indicated for recurrent or metastatic disease. Advances in
[...] Read more.
Salivary gland carcinomas (SGCs) represent a rare and heterogeneous group of malignancies accounting for 3–6% of all head and neck cancers. While surgical resection and radiotherapy remain the standard for locoregional control, systemic treatment is indicated for recurrent or metastatic disease. Advances in molecular profiling have identified actionable targets such as NTRK gene fusions, HER2, immune checkpoint regulators, androgen receptors, and RET receptors. These have facilitated the development of targeted therapies, including TRK inhibitors, HER2-directed agents, and androgen receptor modulators, as well as emerging combinations of immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Despite these advancements, challenges such as resistance mechanisms and limited therapeutic efficacy persist. Overall response rates remain relatively low across most systemic therapies, reflecting a persistent unmet clinical need. This review discusses the current landscape of treatment options and explores promising clinical trials and future directions to enhance outcomes for patients with SGCs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Head and Neck Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction in Patients with Non-Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review
by
Toni Zhong, Glenn G. Fletcher, Muriel Brackstone, Simon G. Frank, Renee Hanrahan, Vivian Miragias, Christiaan Stevens, Danny Vesprini, Alyssa Vito and Frances C. Wright
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 231; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040231 - 16 Apr 2025
Abstract
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy improves the quality of life for many patients with breast cancer. There is uncertainty regarding eligibility criteria for reconstruction, timing (immediate or delayed—with or without radiotherapy), outcomes of nipple-sparing compared to skin-sparing mastectomy, selection criteria and surgical factors influencing
[...] Read more.
Breast reconstruction after mastectomy improves the quality of life for many patients with breast cancer. There is uncertainty regarding eligibility criteria for reconstruction, timing (immediate or delayed—with or without radiotherapy), outcomes of nipple-sparing compared to skin-sparing mastectomy, selection criteria and surgical factors influencing outcomes of nipple-sparing mastectomy, prepectoral versus subpectoral implants, use of acellular dermal matrix, and use of autologous fat grafting. We conducted a systematic review of these topics to be used as the evidence base for an updated clinical practice guideline on breast reconstruction for Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario). The protocol was registered on PROSPERO, CRD42023409083. Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases were searched until August 2024, and 229 primary studies met the inclusion criteria. Most studies were retrospective non-randomized comparative studies; 5 randomized controlled trials were included. Results suggest nipple-sparing mastectomy is oncologically safe, provided there is no clinical, radiological, or pathological indication of nipple-areolar complex involvement. Surgical factors, including incision location, may affect rates of complications such as necrosis. Both immediate and delayed reconstruction have similar long-term outcomes; however, immediate reconstruction may result in better short to medium-term quality of life. Evidence on whether radiotherapy should modify the timing of initial reconstruction or expander-implant exchange was very limited; studies delayed reconstruction after radiotherapy by at least 3 months and, more commonly, at least 6 months to avoid the period of acute radiation injury. Radiation after immediate reconstruction is a reasonable option. Surgical complications are similar between prepectoral and dual-plane or subpectoral reconstruction; prepectoral placement may give a better quality of life due to lower rates of long-term complications such as pain and animation deformity. Autologous fat grafting was found to be oncologically safe; its use may improve quality of life and aesthetic results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
LAG3, TIM3 and TIGIT: New Targets for Immunotherapy and Potential Associations with Radiotherapy
by
Camil Ciprian Mireștean, Roxana Irina Iancu and Dragoș Petru Teodor Iancu
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 230; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040230 - 15 Apr 2025
Abstract
The combination of immunotherapy and radiotherapy has demonstrated synergistic potential, especially when a combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) is administered. Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein-4 (CTLA-4) inhibitors and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitors or Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitors have been assessed
[...] Read more.
The combination of immunotherapy and radiotherapy has demonstrated synergistic potential, especially when a combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) is administered. Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein-4 (CTLA-4) inhibitors and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitors or Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitors have been assessed in both clinical and preclinical studies; the addition of radiotherapy activates immunomodulatory mechanisms materialized by an effect similar to “in situ” vaccination or the “abscopal” distant response of lesions outside the irradiation field. The new therapeutic targets (T cell immune-receptor with Ig and ITIM domains (TIGIT), Lymphocyte activating gene 3 (LAG-3), and T cell Ig- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (TIM-3)) associated with traditional ICIs and radiotherapy open new perspectives to the concept of immuno-radiotherapy. The dynamic evaluation of T lymphocyte expression involved in the antitumor immune response, both in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and in the tumor itself, could have biomarker value in assessing the response to combination therapy with traditional and new ICIs in association with irradiation. Preclinical data justify the initiation of clinical trials in various tumor pathologies to explore this concept.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Evolving Landscape of Precision Medicine in Radiation Oncology)
Open AccessArticle
Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with High PD-L1 Expression
by
Vesna Ćeriman Krstić, Ivan Soldatović, Milija Gajić, Natalija Samardžić, Ruža Stević, Nikola Čolić, Katarina Lukić, Biljana Šeha, Damir Radončić, Slavko Stamenić, Milan Savić, Vladimir Milenković, Brankica Milošević Maračić and Dragana Jovanović
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 229; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040229 - 15 Apr 2025
Abstract
Before the introduction of targeted therapy and immunotherapy, patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) had a 5-year overall survival (OS) rate of up to 10%. After the positive results of KEYNOTE-024, pembrolizumab was approved in a first-line setting for patients with metastatic
[...] Read more.
Before the introduction of targeted therapy and immunotherapy, patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) had a 5-year overall survival (OS) rate of up to 10%. After the positive results of KEYNOTE-024, pembrolizumab was approved in a first-line setting for patients with metastatic NSCLC and PD-L1 ≥ 50%. A small number of patients had a durable response to immunotherapy, and so far it has not been discovered who will benefit. The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of first-line pembrolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic NSCLC with high PD-L1 expression in a real-world setting. We enrolled 35 patients with locally advanced and metastatic NSCLC who had PD-L1 ≥ 50%. Progression-free survival was 9 months, 95% CI (2.6–15.4). Overall survival was 14 months, 95% CI (0–28.5). Five-year OS rate for the whole group of patients was 20%, and the six-year OS rate was 17.2%. Immunotherapy was a revolution in the treatment of NSCLC. We still do not know which patients will benefit from immunotherapy, but patients who do respond may experience long-term outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current State of Immunotherapy for Lung Cancer: Focusing on Real-World Evidence)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Gastric Cancer in the Countryside or in the City: Does the Prognosis Change? An Analysis from the German States of Brandenburg and Berlin
by
Andreas Loew, Anne von Ruesten, Constanze Schneider, René Mantke, Karsten H. Weylandt and Stephan Gretschel
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 228; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040228 - 14 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Medical care structures differ between urban and rural areas. Clinical cancer registries can depict real-world care through detailed data analysis, identifying potential regional disparities and contributing to improvements in healthcare. Methods: Data from the Brandenburg–Berlin Clinical-Epidemiological Cancer Registry for the years of
[...] Read more.
Background: Medical care structures differ between urban and rural areas. Clinical cancer registries can depict real-world care through detailed data analysis, identifying potential regional disparities and contributing to improvements in healthcare. Methods: Data from the Brandenburg–Berlin Clinical-Epidemiological Cancer Registry for the years of diagnosis 2017–2022 were analyzed to assess the epidemiology and real-world care of gastric cancer, including cardia. Brandenburg was compared to Berlin regarding perioperative treatment regimens. The resulting survival benefits were assessed using Kaplan–Meier and Cox regression models. Results: For the years of diagnosis 2017 to 2022, 5805 cases of gastric carcinoma were documented in the cancer registry. Survival data showed no significant differences between Berlin and Brandenburg. Preoperative therapy for cT3/cT4N0 tumors was significantly more common in Berlin (72%) than in Brandenburg (68%). Perioperative therapy was associated with a survival benefit for stages T3-/T4N+ but not for stages T1N+ or T2. The lower proportion of pre-treated T3/T4N+ patients in rural Brandenburg did not result in a significant survival difference. Conclusions: The data provide a comprehensive representation of the current state of gastric cancer care in these two regions. Gastric cancer treatment outcomes, in terms of survival, are comparable between the rural region of Brandenburg and the urban center of Berlin.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastrointestinal Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prognostic and Inflammatory Differences Between Upper and Mid–Lower Rectal Cancers in Non-Metastatic Stage II–II Disease
by
Fırat Mülküt, Cem Batuhan Ofluoğlu, Mustafa Kağan Başdoğan, İsa Caner Aydın, Akif Doğan and İsmail Ege Subaşı
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 227; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040227 - 12 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to compare the clinical, pathological, and biochemical characteristics of upper rectal cancer (URC) and mid–lower rectal cancer (MLRC) in stage II and III non-metastatic rectal cancer and to identify distinct prognostic factors influencing survival and recurrence. Material and Methods:
[...] Read more.
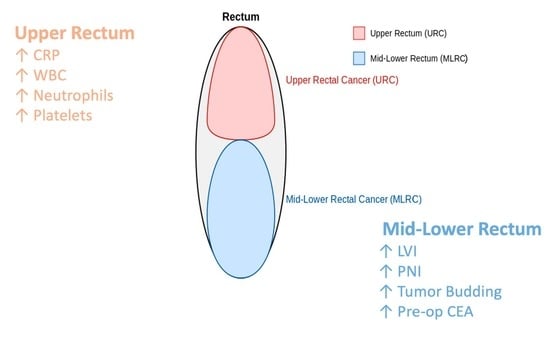
Background: This study aimed to compare the clinical, pathological, and biochemical characteristics of upper rectal cancer (URC) and mid–lower rectal cancer (MLRC) in stage II and III non-metastatic rectal cancer and to identify distinct prognostic factors influencing survival and recurrence. Material and Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 100 patients with stage II and III non-metastatic rectal adenocarcinoma who underwent neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) followed by curative-intent surgery between 2021 and 2024. Patients were categorized into URC (n = 53) and MLRC (n = 47) groups. Parameters analyzed included demographic factors, ASA score, surgical characteristics, pathological features (tumor stage, lymph node involvement, lymphovascular invasion (LVI), perineural invasion (PNI), tumor budding, tumor regression grade (TRG)), and biochemical markers (carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), white blood cell (WBC) count, neutrophil count, platelet count (PLT), and C-reactive protein (CRP)). One-year overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were analyzed using Kaplan–Meier survival curves, and Cox regression models identified independent prognostic factors. Results: Preoperative CEA levels were higher in MLRC (p = 0.05), whereas WBC count (p = 0.01), neutrophil count (p = 0.02), PLT (p = 0.01), and CRP levels (p = 0.01) were higher in URC. Pathological analysis revealed higher LVI (p = 0.04), PNI (p = 0.04), and tumor budding (p = 0.03) in MLRC. At one-year follow-up, OS rates were 82.1% (URC) vs. 80.3% (MLRC) (p = 0.85), and DFS rates were 78.6% (URC) vs. 73.4% (MLRC) (p = 0.72). Multivariate Cox regression analysis identified age (HR: 1.04, p = 0.03), ASA score (HR: 1.22, p = 0.01), CRP (HR: 1.18, p < 0.001), preoperative CEA (HR: 1.12, p = 0.02), preoperative CA19-9 (HR: 1.09, p = 0.03), LVI (HR: 1.42, p < 0.001), PNI (HR: 1.35, p = 0.02), and tumor budding (HR: 1.28, p = 0.03) as independent prognostic factors for OS. Similar trends were observed for DFS, with T stage (HR: 1.35, p = 0.01) and tumor size (HR: 1.22, p = 0.01) also being found significant. Conclusions: Inflammatory markers, tumor burden indicators (LVI, PNI, budding, tumor size, T stage), and preoperative CEA/CA19-9 were identified as significant predictors, suggesting a risk-adapted approach to rectal cancer treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastrointestinal Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Modern Treatment of Skeletal Metastases: Multidisciplinarity and the Concept of Oligometastasis in the Recent Literature
by
Giulia Trovarelli, Arianna Rizzo, Felicia Deborah Zinnarello, Mariachiara Cerchiaro, Andrea Angelini, Elisa Pala and Pietro Ruggieri
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 226; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040226 - 11 Apr 2025
Abstract
Bone metastases are a major concern in cancer management since they significantly contribute to morbidity and mortality. Metastatic lesions, commonly arising from breast, prostate, lung, and kidney cancers, affect approximately 25% of cancer patients, leading to severe complications such as pain, fractures, and
[...] Read more.
Bone metastases are a major concern in cancer management since they significantly contribute to morbidity and mortality. Metastatic lesions, commonly arising from breast, prostate, lung, and kidney cancers, affect approximately 25% of cancer patients, leading to severe complications such as pain, fractures, and neurological deficits. This narrative review explores contemporary approaches to bone metastases, emphasizing a multidisciplinary strategy and the evolving concept of oligometastatic disease. Oligometastases, defined by limited metastatic spread (1–5 lesions), offer a potential window for curative treatment through aggressive interventions, including stereotactic ablative radiotherapy and resection surgery. Tumor boards, integrating systemic therapies with local interventions, are crucial to optimize treatment. Despite promising results, gaps remain in defining optimal treatment sequences and refining patient selection criteria. Future research should focus on personalized approaches, leveraging biomarkers and advanced imaging to enhance outcomes and the quality of life in patients with bone metastases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue 2nd Edition: Treatment of Bone Metastasis)
Open AccessSystematic Review
A Systematic Review of Cost-Effectiveness Studies on Pancreatic Cancer Screening
by
Diedron Lewis, Laura Jiménez, Kelvin K. Chan, Susan Horton and William W. L. Wong
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 225; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040225 - 11 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer (PC) is among the deadliest types of cancer globally. While early detection helps avert adverse outcomes, screening is only recommended for individuals at high risk, specifically those with familial and/or genetic predispositions. The objectives of this study are to systematically
[...] Read more.
Background: Pancreatic cancer (PC) is among the deadliest types of cancer globally. While early detection helps avert adverse outcomes, screening is only recommended for individuals at high risk, specifically those with familial and/or genetic predispositions. The objectives of this study are to systematically review primary studies on the cost-effectiveness of PC screening and to identify the critical factors that influence cost-effectiveness. Methods: This systematic review was performed using PRISMA guidelines. Economic evaluation studies on PC screening were identified from searches on the SCOPUS and PubMed databases. The quality of reporting of the selected articles was assessed according to CHEERS 2022. Using predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, two reviewers conducted the title–abstract review, full-text review, and data extraction to select relevant articles. The authors’ consensus was used to settle disagreements. The primary outcome was the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio, measured by cost per quality-adjusted life year and cost per life year saved. Results: Nine studies were selected for the final review. Most studies demonstrated that one-time screening for PC among high-risk individuals was cost-effective compared with no screening, while others found annual screening to also be cost-effective. High-risk was generally defined as having a >5% lifetime risk of PC and included individuals with either familial pancreatic cancer (FPC) or genetic susceptibility syndromes such as Peutz–Jeghers Syndrome, hereditary pancreatitis, hereditary non-polypoid colorectal cancer syndrome, familial adenomatous polyposis, and BRCA2 mutations. Individuals with new-onset diabetes (NOD) were also considered high-risk. Screening using mainly endoscopic ultrasound was cost-effective among FPC individuals and those with genetic syndromes. Risk-based screening was also cost-effective among patients with NOD. Conclusion: Screening for PC is cost-effective among selected high-risk individuals. However, cost-effectiveness depends on epidemiological factors, cost, the diagnostic performance of screening tools, and the overall design of studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Health Economics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Folliculin (FLCN) in Thyroid Tumors: Incidence, Significance, and Role as a Driver Gene and Secondary Alteration
by
Faisal A. Hassan, Camryn Slone, Robert J. McDonald, Julie C. Dueber, Adeel M. Ashraf, Melina J. Windon, Oliver J. Fackelmayer, Cortney Y. Lee, Therese J. Bocklage and Derek B. Allison
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 224; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040224 - 11 Apr 2025
Abstract
Thyroid carcinomas are driven by diverse molecular alterations, but the tumor suppressor gene folliculin (FLCN), best known for its role in Birt–Hogg–Dubé (BHD) syndrome, has received limited attention in thyroid tumors. Here, we describe two thyroid tumors with pathogenic FLCN alterations—one
[...] Read more.
Thyroid carcinomas are driven by diverse molecular alterations, but the tumor suppressor gene folliculin (FLCN), best known for its role in Birt–Hogg–Dubé (BHD) syndrome, has received limited attention in thyroid tumors. Here, we describe two thyroid tumors with pathogenic FLCN alterations—one germline and one somatic—and analyze the broader prevalence and significance of FLCN in thyroid carcinomas using multiple large sequencing datasets, including ORIEN-AVATAR. Patient 1, with a germline FLCN mutation and a history of BHD syndrome, presented with a well-circumscribed oncocytic adenoma. Molecular testing confirmed biallelic FLCN inactivation, but no additional mutations or aggressive features were observed, and the patient remained disease-free post-thyroidectomy. Patient 2 harbored a somatic FLCN mutation in an oncocytic poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma, which exhibited extensive angioinvasion, high proliferative activity, and concurrent TP53 and RB1 mutations. The tumor progressed with metastatic disease despite multimodal treatment. Thyroid carcinomas revealed FLCN alterations in 1.1% of cases. Pathogenic mutations were rare but associated with oncocytic morphology, while homozygous deletions occurred more frequently in genomically unstable tumors, including anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. These findings suggest FLCN mutations may act as early oncogenic drivers in oncocytic thyroid neoplasms, while deletions represent secondary events in aggressive tumor evolution. The lack of FLCN coverage in standard thyroid molecular panels likely underestimates its clinical relevance. Including FLCN in genetic testing could improve tumor detection and characterization, particularly in BHD patients who may benefit from routine thyroid screening. Further studies are needed to clarify FLCN’s role in thyroid cancer pathogenesis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue 2nd Edition: Molecular Testing for Thyroid Nodules and Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Computed Tomography-Based Radiomic Nomogram to Predict Occult Pleural Metastasis in Lung Cancer
by
Xiaoyi Zhao, Heng Zhao, Kongxu Dai, Xiangyu Zeng, Yun Li, Feng Yang and Guanchao Jiang
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 223; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040223 - 11 Apr 2025
Abstract
Objectives: The preoperative identification of occult pleural metastasis (OPM) in lung cancer remains a crucial clinical challenge. This study aimed to develop and validate a predictive model that integrates clinical information with chest CT radiomic features to preoperatively identify patients at risk of
[...] Read more.
Objectives: The preoperative identification of occult pleural metastasis (OPM) in lung cancer remains a crucial clinical challenge. This study aimed to develop and validate a predictive model that integrates clinical information with chest CT radiomic features to preoperatively identify patients at risk of OPM. Methods: This study included 50 patients diagnosed with OPM during surgery as the positive training cohort and an equal number of nonmetastatic patients as the negative control cohort. Using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression, we identified key radiomic features and calculated radiomic scores. A predictive nomogram was developed by combining clinical characteristics and radiomic scores, which was subsequently validated with data from an additional 545 patients across three medical centers. Results: Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses revealed that carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the clinical T stage, and the tumor–pleural relationship were significant clinical predictors. The clinical model alone achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.761. The optimal integrated model, which combined radiomic scores from the volume of interest (VOI) with the CEA and NLR, demonstrated an improved predictive performance, with AUCs of 0.890 in the training cohort and 0.855 in the validation cohort. Conclusions: Radiomic features derived from CT scans show significant promise in identifying patients with lung cancer at risk of OPM. The nomogram developed in this study, which integrates CEA, the NLR, and radiomic tumor area scores, enhances the precision of preoperative OPM prediction and provides a valuable tool for clinical decision-making.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Thoracic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Primary Central Nervous System Tumors in Adolescents: A Population-Based Study on Epidemiology and Clinical Pathways in a Challenging Age Group
by
Lucia De Martino, Patrizia Piga, Marcella Sessa, Camilla Calì, Camilla Russo, Stefania Picariello, Nicola Onorini, Pietro Spennato, Lucia Quaglietta, Maria Vittoria Donofrio, Giuseppe Cinalli, Francesco Vetrano and Fabio Savoia
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 222; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040222 - 10 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Oncological care of adolescent patients is often inconsistent, as they frequently fall between pediatric and adult services. The Childhood Cancer Registry of Campania (CCRC) is the Italian largest population-based registry specializing in children 0–19 years old, with a target population of approximately
[...] Read more.
Background: Oncological care of adolescent patients is often inconsistent, as they frequently fall between pediatric and adult services. The Childhood Cancer Registry of Campania (CCRC) is the Italian largest population-based registry specializing in children 0–19 years old, with a target population of approximately 1.1 million inhabitants. Material and Methods: This report presents epidemiological indicators and clinical pathways on primary brain tumors in adolescents (15–19 years) from the Campania region. Results: Over the study period (2008–2020), the cohort included 219 adolescents with newly diagnosed central nervous system (CNS) tumors with an annual average incidence rate (IR) of 48.9 cases per million/year. The 5-year observed survival rate after diagnosis of CNS tumor was 84.8%. Overall, the most common tumor site was the pituitary gland and craniopharyngeal duct, representing 22.4% of all tumors. The most frequently occurring malignant primary CNS tumor was germinoma, while the most common non-malignant tumor was pituitary adenoma. Most patients were referred to adult services and nearly half migrated outside the region to receive cancer care. Conclusions: Challenges in the care of adolescent oncology patients include limited access to specialized care, difficulties in transitioning from pediatric to adult institutions, distinct tumor biology, and the underrepresentation of adolescents in clinical trials. The care of adolescents with CNS tumors is fragmented across institutions and significant variations in practice exist between adult and pediatric practitioners.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Quality of Life and Follow-Up Care Among AYA Cancer Survivors)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Developing the Understanding Palliative Care Module: A Quality Improvement Initiative Incorporating Public, Patient, and Family Caregiver Perspectives
by
Patricia Biondo, Mary-Ann Shantz, Yuanjie (Bill) Zheng, Miranda Manning and Louise Kashuba
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 221; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040221 - 10 Apr 2025
Abstract
Improving public awareness of palliative care is crucial for improving access to, and uptake of, palliative care, which has demonstrated benefits for patients and health systems. However, there is a lack of engaging, accessible educational palliative care resources designed for public audiences. As
[...] Read more.
Improving public awareness of palliative care is crucial for improving access to, and uptake of, palliative care, which has demonstrated benefits for patients and health systems. However, there is a lack of engaging, accessible educational palliative care resources designed for public audiences. As part of a larger quality improvement initiative to strengthen awareness of palliative care, we developed “Understanding Palliative Care”—an innovative, online educational module incorporating best practices for defining and promoting palliative care to a public audience. An expert working group with representation from nursing, medicine, social work, instructional design, and care navigation advised on the development of the module. Incorporating the perspectives of Albertans with lived palliative care experience was deemed essential by the working group. We identified three Albertans (one patient and two family caregivers) of diverse ages and cultural backgrounds who had personally benefitted from palliative care and consented to record virtual interviews. We incorporated multiple interview segments into the module that highlight the physical, emotional, social, and spiritual support provided by palliative care. Finally, a panel of thirteen public volunteers provided feedback on the content, design, and navigation of the draft module. The Understanding Palliative Care module fills an important gap in Alberta, providing a free, online, evidence-based, and engaging educational tool to improve public awareness and understanding of palliative care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Building Hope for the Next Decade of Psychosocial Oncology: Optimizing the Integration of Supportive Care into Oncology Care)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Dysphagia on Head and Neck Cancer Patients’ Quality of Life, Functional Disabilities and Psychological Distress: Outcomes of Cancer Rehabilitation from an Observational Single-Center Study
by
Špela Matko, Christina Knauseder, David Riedl, Vincent Grote, Michael J. Fischer, Samuel Moritz Vorbach, Karin Pfaller-Frank, Wilhelm Frank and Thomas Licht
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 220; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040220 - 10 Apr 2025
Abstract
Many patients with head-and-neck cancer (HNC) suffer from speech or swallowing disorders. We investigated the impact of dysphagia on health-related quality of life (HRQOL), functioning, and distress in HNC survivors, and whether cancer rehabilitation can alleviate these conditions. Before admission (T0) and at
[...] Read more.
Many patients with head-and-neck cancer (HNC) suffer from speech or swallowing disorders. We investigated the impact of dysphagia on health-related quality of life (HRQOL), functioning, and distress in HNC survivors, and whether cancer rehabilitation can alleviate these conditions. Before admission (T0) and at discharge (T1) of three-week inpatient cancer rehabilitation, patient-reported outcomes were collected. HRQOL, symptoms, functioning, and psychological distress were assessed with EORTC QLQ-C30 and Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) questionnaires. Of 63 HNC patients, 22 had dysphagia, 23 needed no speech therapy (Control-1), and 18 needed speech therapy, but showed no symptoms of dysphagia (Control-2). Before rehabilitation, HRQOL, physical, social, and emotional functioning were significantly lower in dysphagia patients than in controls. Dysphagia patients reported more severe general symptoms including fatigue, pain, sleep disturbances, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, and financial worries. Furthermore, the emotional and social functioning of Control-2 was significantly worse than Control-1. For all HNC patients, social, emotional, and role functioning, fatigue, nausea/vomiting, insomnia, and appetite loss significantly improved at T1. Improvements in HRQOL were most noticeable in dysphagia patients. Psychooncological counseling reduced depression in dysphagia and Control-2 patients to levels seen in the general population. In conclusion, dysphagia patients suffer severely from impaired functioning and systemic symptoms but benefit substantially from rehabilitation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Head and Neck Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
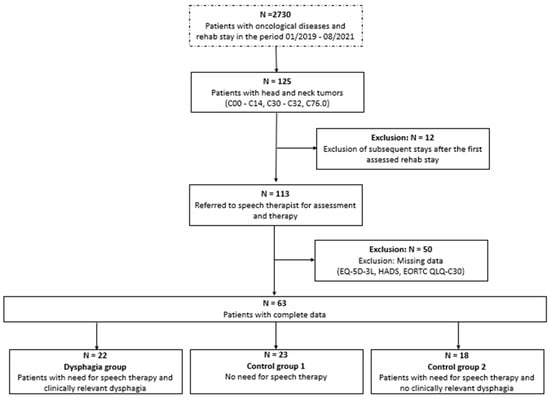
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A Rare Malignant Case of a Primary Pseudomyogenic Haemangioendothelioma of the Bone
by
Annabella Di Mauro, Salvatore Tafuto, Lucia Cannella, Francesca Collina, Giovanni Neri, Ottavia Clemente, Imma D’Arbitrio, Francesca Ricci, Secondo Lastoria, Gerardo Ferrara and Annarosaria De Chiara
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 219; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040219 - 10 Apr 2025
Abstract
Pseudomyogenic haemangioendotheliomas (PMH) are exceedingly rare, mostly occurring in soft tissue, with malignant cases even more uncommon. In this report, we present a case of a 28-year-old male initially suspected of having a fibroblastic osteosarcoma of the right femur, which was then correctly
[...] Read more.
Pseudomyogenic haemangioendotheliomas (PMH) are exceedingly rare, mostly occurring in soft tissue, with malignant cases even more uncommon. In this report, we present a case of a 28-year-old male initially suspected of having a fibroblastic osteosarcoma of the right femur, which was then correctly diagnosed as a primary pseudomyogenic hemangioendothelioma of the bone with synchronous metastases to other skeletal segments. Molecular analysis through targeted RNA sequencing confirmed the correct diagnosis, revealing a fusion transcript ACTB::FOSB. To our knowledge, this is one of the few reported cases of suffering from multiple pathological fractures. The rapid skeletal progression and the onset of distant metastases in this case is highly unusual considering the typically indolent clinical course commonly reported in the literature for this tumor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bone and Soft Tissue Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A Rare Case of Non-Hodgkin B-Cell Lymphoma Following Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: A Case Report
by
Elisa Bertulla, Raquel Diaz, Matteo Mascherini, Marco Casaccia, Francesca Depaoli, Letizia Cuniolo, Chiara Cornacchia, Cecilia Margarino, Federica Murelli, Simonetta Franchelli, Marianna Pesce, Chiara Boccardo, Marco Gipponi, Franco De Cian and Piero Fregatti
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 218; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040218 - 10 Apr 2025
Abstract
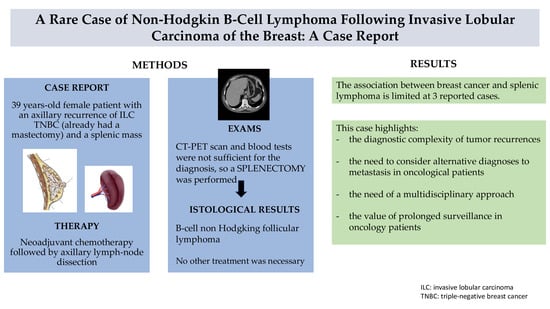
The association between breast cancer and non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the spleen is extremely rare, with very few cases documented in the medical literature. We present the case of a 39-year-old woman in good health but with a family history of breast cancer, who,
[...] Read more.
The association between breast cancer and non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the spleen is extremely rare, with very few cases documented in the medical literature. We present the case of a 39-year-old woman in good health but with a family history of breast cancer, who, in 2017, developed invasive lobular carcinoma in her right breast, which was treated with mastectomy followed by hormonal therapy. In 2024, she presented with a suspicious right axillary mass, suspected of recurrence, which was confirmed by fine-needle aspiration biopsy. The patient received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, followed by axillary lymph node dissection and bilateral adnexectomy. CT and PET scans showed suspicious splenic lesions suggestive of metastases. Infectious and hematological tests were negative, leading to the decision to perform laparoscopic splenectomy. Histological examination revealed follicular B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The patient is now in good general condition and is on a biannual follow-up. The case highlights the diagnostic complexity of tumor recurrences and the need to consider alternative diagnoses other than metastasis in oncological patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Low-Malignant-Potential Adenocarcinoma: A Histological Category with a Significantly Better Prognosis than Other Solid Adenocarcinomas at IA Stage
by
Marco Chiappetta, Alessandra Cancellieri, Filippo Lococo, Elisa Meacci, Carolina Sassorossi, Maria Teresa Congedo, Qianqian Zhang, Diomira Tabacco, Isabella Sperduti and Stefano Margaritora
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 217; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040217 - 9 Apr 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Low-malignant-potential adenocarcinoma has been defined as a type of non-mucinous tumor, which has a total tumor size measuring ≤ 3 cm, exhibits ≥ 15% lepidic growth, lacks non-predominant high-grade patterns (≥10% cribriform, ≥5% micropapillary, ≥5% solid), has an absence of angiolymphatic or
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Low-malignant-potential adenocarcinoma has been defined as a type of non-mucinous tumor, which has a total tumor size measuring ≤ 3 cm, exhibits ≥ 15% lepidic growth, lacks non-predominant high-grade patterns (≥10% cribriform, ≥5% micropapillary, ≥5% solid), has an absence of angiolymphatic or visceral pleural invasion, spread through air spaces (STAS), necrosis and >1 mitosis per 2 mm2. The aim of this study is to validate, with regard to cancer-specific survival (CSS) and disease-free survival (DFS), the proposed definition of LMP adenocarcinoma in an independent external cohort of lung adenocarcinoma patients having undergone surgical resection, and having presented with a long follow-up period. Methods: Clinicopathological characteristics of patients who underwent lung resection for adenocarcinoma from 1 January 2005 to 31 December 2014 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients with ground-glass opacity (GGO) and part-solid tumors, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma (MIA), adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS), tumors ≥5 cm in size, nodal involvement and/or distant metastases, patients who underwent neoadjuvant treatment, and those who had an incomplete follow-up or a follow-up shorter than 60 months were excluded. The proposed criteria for low-malignant-potential adenocarcinoma (LMPA) were tumor size ≤ 3 cm, invasive size ≥ 0,5 cm, lepidic growth ≥ 15%, and absence of the following: mitosis (>1 per 2 mm2), mucinous subtype, angiolymphatic invasion, visceral pleural invasion, spread through air spaces (STAS) and tumor necrosis. End points were disease-free survival (DFS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS). The log-rank test was used to assess differences between subgroups. Results: Out of 80 patients meeting the proposed criteria, 14 (17.5%) had the LMPA characteristics defined. The mean follow-up time was 67 ± 39 months. A total of 19 patients died, all in the non-LMPA category, and 33 patients experienced recurrence: 4 (28.5%) with LMPA and 29 (43.9%) with non-LMPA. Log-rank analysis showed 100% 10-year CSS for patients with LMPA and 77.4% for patients without LMPA, with this difference being statistically significant (p-value = 0.047). Univariate analysis showed a significant association with the cStage (AJCC eighth edition), both for CSS (p value = 0.005) and DFS (p-value = 0.003). LMPA classification did not show a statistically significant impact on CSS and DFS, likely due to the limited number of events (CSS p-value = 0.232 and DFS p-value = 0.213). No statistical association was found for CSS and DFS with pT, the number of resected nodes (< or >10) or the number of resected N2 stations (< or >2). Conclusions: Our study confirmed the prognostic role of LMPA features, with a low risk of recurrence and a good CSS and DFS. The criteria for diagnosis are replicable and feasible for application. The clinical implications of these findings, such as pre-operative prediction and surveillance scheduling, may be the topic of future prospective studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Current Status of Lung Cancer Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures
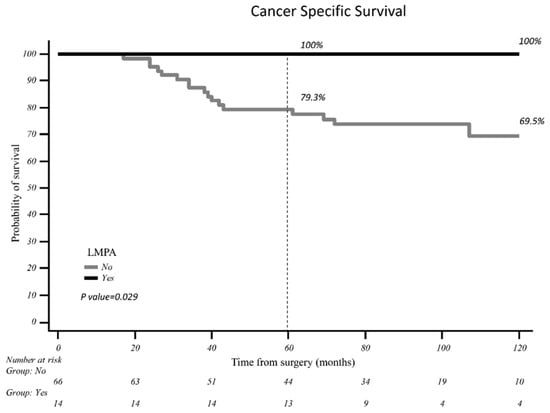
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Using Invitation Letters to Increase HPV Vaccination Among Adult Women
by
Kelly Bunzeluk, Laura Coulter, Donna Turner, Chaeyoon Jeong, Carla Krueger and Austin Hill
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 216; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040216 - 9 Apr 2025
Abstract
(1) Background: In Manitoba, most people get the HPV vaccine through a publicly funded school-based program. If they miss the school-based program, they remain eligible for the free HPV immunization program. This study explored whether invitation and reminder letters would increase HPV vaccine
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: In Manitoba, most people get the HPV vaccine through a publicly funded school-based program. If they miss the school-based program, they remain eligible for the free HPV immunization program. This study explored whether invitation and reminder letters would increase HPV vaccine uptake among adult women who remained eligible for the publicly funded program. (2) Methods: Eligible individuals were randomized into three groups of 4650 women each. Intervention groups I and II were mailed an information package inviting them to be vaccinated. Six weeks later, intervention group II received a reminder letter if they remained unvaccinated. The control group received no correspondence related to HPV vaccination. Vaccination status, defined as at least one dose of an approved HPV vaccine, was calculated six months after the packages were mailed. (3) Results: Overall, 4.0% (3.4–4.6%, p < 0.0001) of individuals in intervention group II (invitation/reminder) and 2.5% (2.1–3.0%, p < 0.0001) of individuals in intervention group I (invitation) received one dose of the HPV vaccine. Compared to the control group, sending invitations/reminders and invitation packages increased the likelihood of getting at least one dose of the HPV vaccine by 4.9 times (3.4–6.9, p < 0.0001) and 3.0 times (2.1–4.4, p < 0.0001), respectively. (4) Conclusion: Sending invitation and reminder letters to unvaccinated women may be an effective and low-cost way to increase HPV vaccination coverage among adults who are eligible for the publicly funded immunization program.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Action and Impact: Prevention and Screening Strategies Contributing to the Elimination of Cervical Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
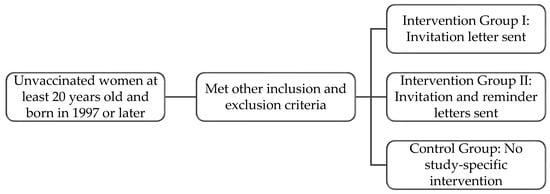
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Current Limitations of Sentinel Node Biopsy in Vulvar Cancer
by
Myriam Gracia, Maria Alonso-Espías and Ignacio Zapardiel
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 215; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040215 - 8 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Vulvar cancer is a rare gynecologic malignancy with increasing incidence. Lymph node status is the most critical prognostic factor, traditionally assessed through inguinofemoral lymphadenectomy, a procedure associated with significant morbidity. Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB), in selected cases, has emerged as a
[...] Read more.
Background: Vulvar cancer is a rare gynecologic malignancy with increasing incidence. Lymph node status is the most critical prognostic factor, traditionally assessed through inguinofemoral lymphadenectomy, a procedure associated with significant morbidity. Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB), in selected cases, has emerged as a less invasive alternative with favorable oncologic outcomes. Objective: This review summarizes current evidence on the indications, technique, safety, and oncologic outcomes of SLNB in vulvar cancer, with a focus on controversial scenarios such as recurrent and larger tumors. Methods: A narrative review of PubMed-indexed studies published in English over the last 35 years was conducted. Eligible studies included original research, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, and case-control studies. Results: SLNB is recommended for unifocal vulvar tumors < 4 cm with stromal invasion > 1 mm and clinically negative nodes. Landmark trials, including GROINSS-V-I and GOG-173, confirmed its accuracy and lower morbidity compared to lymphadenectomy. SLNB utilization has increased since its inclusion in guidelines, with a concurrent decline in lymphadenectomy rates. Combined detection techniques are mandatory, while indocyanine green (ICG) is an emerging option. Future studies should focus on refining patient selection criteria, improving detection techniques, and clarifying the implications of low-volume nodal disease to further optimize outcomes for patients with vulvar cancer. Conclusion: SLNB is a validated, minimally invasive staging approach in early-stage vulvar cancer. Further research is needed to refine its role in high-risk cases and optimize detection methods.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gynecologic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
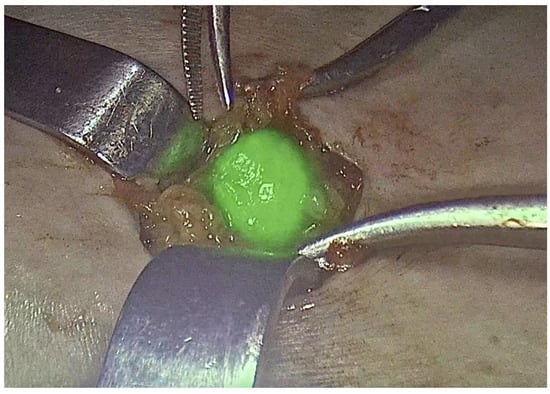
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Survivorship Considerations and Management in the Adolescent and Young Adult Sarcoma Population: A Review
by
Allison Gunderson, Miriam Yun, Babe Westlake, Madeline Hardacre, Nicholas Manguso and Alicia A. Gingrich
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(4), 214; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040214 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Soft tissue sarcoma (STS) has an 2–8% incidence for all malignant tumors in the adolescent and young adult (AYA) population, which are patients from ages 15 to 39. As most STS tumors are aggressive, they require multimodal management with surgery, radiation and chemotherapy.
[...] Read more.
Soft tissue sarcoma (STS) has an 2–8% incidence for all malignant tumors in the adolescent and young adult (AYA) population, which are patients from ages 15 to 39. As most STS tumors are aggressive, they require multimodal management with surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. This article discusses the survivorship considerations in this young population of cancer patients who complete therapy. The lasting side effects include surgical and radiation-related morbidity, chemotherapy toxicity, early and late secondary effects on other organ systems, such as cardiac and endocrine dysfunction, and the development of secondary cancers. The long-term psychologic and practical impacts for those who have received a sarcoma diagnosis in the prime of their life include fertility, mental health, relationship, education and career implications. Although there is a paucity of data in some of these areas, we present existing management guidelines as available. This article serves as a comprehensive review of this wide array of treatment effects intended for all providers participating in the care of AYA sarcoma survivors, to include oncologists, primary care providers and therapists.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Quality of Life and Follow-Up Care Among AYA Cancer Survivors)
►▼
Show Figures
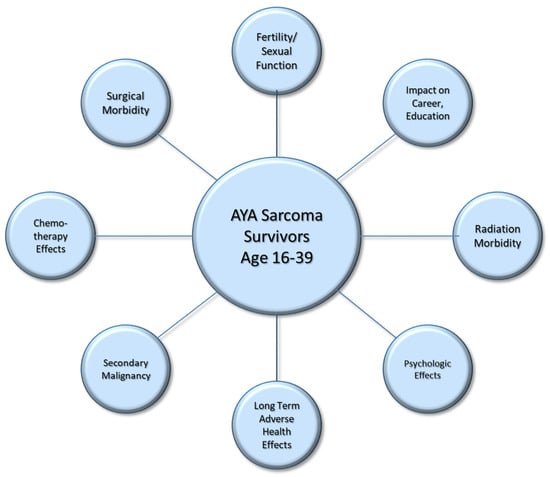
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Current Oncology Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Cancers, Cells, JCM, Radiation, Pharmaceutics, Applied Sciences, Nanomaterials, Current Oncology
Innovative Radiation Therapies
Topic Editors: Gérard Baldacchino, Eric Deutsch, Marie Dutreix, Sandrine Lacombe, Erika Porcel, Charlotte Robert, Emmanuelle Bourneuf, João Santos Sousa, Aurélien de la LandeDeadline: 30 April 2025
Topic in
Biomedicines, Current Oncology, Diagnostics, Gastrointestinal Disorders, JCM, Livers, Transplantology
Advances in Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: From Physiological Mechanisms to Clinical Practice
Topic Editors: Davide Giuseppe Ribaldone, Gian Paolo CavigliaDeadline: 20 June 2025
Topic in
Biomolecules, CIMB, Sci. Pharm., Cancers, Current Oncology, Cells
The Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Modulators of the Tumor Microenvironment
Topic Editors: Nils Ludwig, Miroslaw J SzczepanskiDeadline: 30 June 2025
Topic in
Cancers, Diagnostics, JCM, Current Oncology, Gastrointestinal Disorders, Biomedicines, Therapeutics
Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases: Novel Strategies of Diagnosis and Treatments
Topic Editors: Alessandro Coppola, Damiano Caputo, Roberta Angelico, Domenech Asbun, Chiara MazzarelliDeadline: 20 August 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Evolution of Treatments of Prostate Cancer: From Biology to Current Advanced Technologies
Guest Editor: Fernando MunozDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Cost Effectiveness vs. Affordability in the Age of Targeted Drug Therapies
Guest Editor: Ramy SalehDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Sarcoma Surgeries: Oncological Outcomes and Prognostic Factors
Guest Editor: Mai-Kim GervaisDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Biomarkers and Precision Medicine in Upper Gastrointestinal Malignancies
Guest Editor: Morten LadekarlDeadline: 30 April 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
New Insights into Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editor: Sazan Rasul
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
New Insights into Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editors: Filippo Pesapane, Matteo Suter
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series in "Exercise and Cancer Management"
Collection Editors: Linda Denehy, Ravi Mehrotra, Nicole Culos-Reed
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Contemporary Perioperative Concepts in Cancer Surgery
Collection Editors: Vijaya Gottumukkala, Jörg Kleeff






